OPEN ASSEMBLY
Experiments in Aesthetics and Politics
























[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
[ pending ]
On April 29, 2021, Mer Maggie Roberts and Nandita Biswas Mellamphy gave public lectures as part of the West Hollywood Aesthetics and Politics (WHAP) series. Nandita Biswas Mellamphy, whose work is the focus of this post, is an Associate Professor of Political Science at Western University in London, Ontario. The Spring 2021 Lecture Series, “The Game of the Real: Art and the Knowledge Project,” is presented by the CalArts School of Critical Studies and the West Hollywood Public Library. The lecture can be viewed here.
In the opening moments of Nandita Biswas Mellamphy’s short film Larval Warfare, a voice (likely that of Mellamphy herself) informs us of a novel, impending violence: “A kind of warfare is emerging that is not designed to be visible and spectacular, but rather imperceptible and obscure.”[1] As the voice speaks over fast-moving footage splices from The Matrix, viewers quickly infer that this new form of warfare—whatever it is—is likely as vast and powerful as the matrix itself. Mellamphy describes this emergent construct of warfare as “larval.” Unlike traditional forms of organized conflict, larval warfare is “strategically imperceptible” and largely occurs in unconventional and nonphysical spaces, such as on the Internet.[2]
Mellamphy goes on to explain that larval warfare is made powerful by its vagueness and its ability to “mimic peacetime behaviors” in seemingly-benign digitized spaces, such as social media and online gaming platforms.[3] As such online mechanisms have come to mediate, document, track, and infiltrate nearly every aspect of people’s lives, it is now possible to go to war without declaring it. At first, the phenomenon Mellamphy articulates evokes the architectural Panopticon as a diffused form of discipline, wherein surveillance is invisibilized and omnipresent. The cops are nowhere, which means they are everywhere. But unlike the Panopticon, which remains in a static position at the center of the prison, larval warfare pervades and supersedes borders—be they material or immaterial, physical or digital, private or public:
When warfare becomes larval, it can surreptitiously creep, seep, and sweep into the very micro-processes of everyday life to become normalized. Larval warfare ‘blends in’ with the ordinary and can mimic, exploit, and weaponize ordinary behaviours to gain advantage over opponents. Instead of using force against opponents, action is transformed into techniques that are not evidently coercive or disciplinary.[4]
Larval warfare operates so discreetly, so gently, that its identified “opponents” do not realize the depth of their own manipulation. What’s more, because of the unique ability of these mechanisms to seamlessly “blend in” with the mundane features of the Internet, people often do not perceive they are being manipulated, watched, or exploited at all. It is, in its myriad forms, only legible from its own side, like one-way glass in an interrogation room. Larval warfare disguises itself so well that it becomes inescapable. This all-encompassing mystery gives it a spectral quality; as a ghost haunts a house, those who carry out larval warfare elusively and totally infiltrate the quotidian—which, more often than not, means the intimate.
Mellamphy draws on several contemporarily-familiar verbs to provide examples of activities associated with larval warfare, several of which are familiar to the Internet lexicon: “surfing, tagging, and poking.”[5] These activities allow for “covert surveillance, tracking, and targeting,” enacted in order to influence the interpersonal relationships and opinions of everyday people.[6] Considering the deeply intimate nature of larval warfare and its appropriation of the everyday activities that take place online all over the world, I am compelled to consider how existing within a “larval” digitized world could be expressed. More specifically, I am interested in how the experience and affective consequences of larval warfare could be rendered in art, using the very formats it relies upon to be effective. To give treatment to these ultra-contemporary questions, I am compelled to return to a much more analog form: the novel.
Larval Warfare and Dennis Cooper’s Zac’s Haunted House
Zac’s Haunted House is a “novel” written entirely in the looped visual images of GIFs. Written in 2015 by American writer Dennis Cooper, it is a novel in the loose sense that its narrative structure does not parallel real events or people. But because the novel is GIFs and GIFs alone, the absence of language and reliance on visual information destabilizes its categorization. Brief-reaction GIFs featuring microclips of popular media or flashy moving text have made them extremely popular on social media platforms like Twitter and Instagram. GIFs are gestural, crystallized affects that often make specific cultural references. This gives the format an all-encompassing appropriateness, able to respond to an infinite number of interpersonal situations and broader cultural, social, and political phenomena. The GIFs Cooper uses evoke paranoia, horror, fear, and gore, while also incorporating topical Internet humor and irony into each chapter. In this sense, Zac’s Haunted House narrativizes as larval warfare manipulates: using immediately recognizable digital forms to obfuscate “reality” and noiselessly blend into Internet mundanity.
As larval warfare makes irrelevant the existing divisions between the categories of “military” and “civilian,” Cooper uses GIFs to blur the boundaries between genuine and performed emotion.[7] In a 2015 interview with The New Yorker, Cooper describes how he finds working with GIFs “weirdly very emotional,” as the form allows for “fictional emotional displays and ‘real’ displays are made indistinguishable.”[8] This blurring of boundaries is reminiscent of what Mellamphy calls “thresholds of ambiguity,” wherein larval warfare leads to an eventual conflation between expert knowledge and popular culture, and a dissolution of the distinction between war and peace.[9] When one of these images are created, Cooper believes readers and viewers are “left with something that feels a little bit ‘real,’ a little bit ‘fictional,’ and […] a little bit neither.”[10]
Throughout the “novel,” Cooper combines hyperrealistic terror with more innocuous representations of the same action or event. In the second chapter, the action is the fall. Within the continuous scroll of GIFs, a funny or cute GIF will be followed by another that is creepy at best and existentially terrifying at worst. All of the GIFs comprising the second chapter deal in some way with free fall, a loss of balance, contact with the ground, accident and intention; leaping from a building perhaps expecting to fly, a fear of falling, the silent scream of free fall juxtaposed with the silence immediately following the end of the fall.





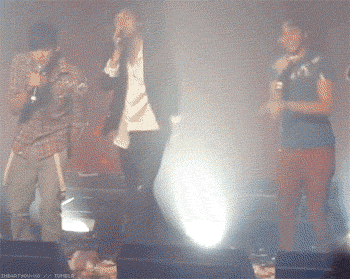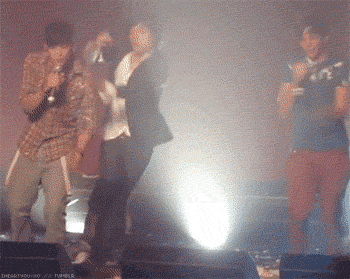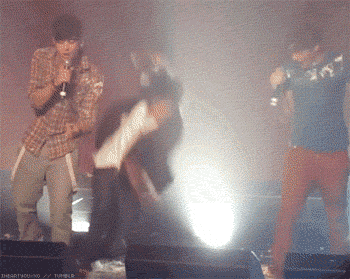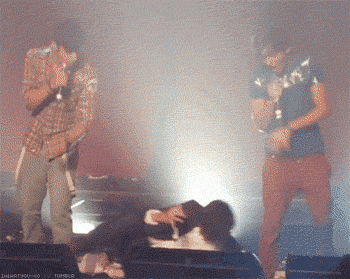






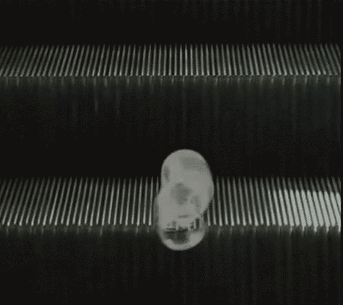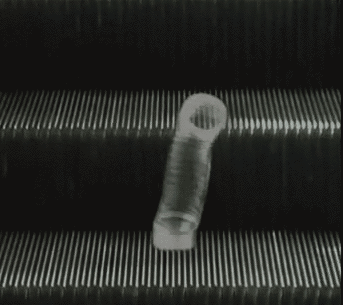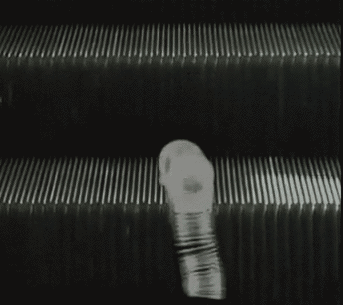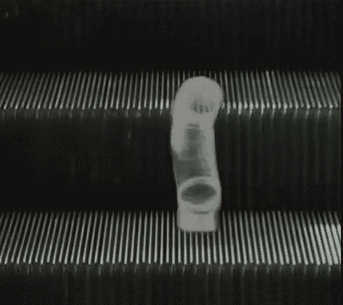




The first few opening sections to Dennis Cooper’s GIF novel Zac’s Haunted House.
Though the presentation changes, the action of the fall is present in each scene; a breakdancer misses his landing, then a person falls, violently, from the top of what appears to be the Chrysler Building. A slinky falls perpetually down an escalator, a cat falls but regains balance. A handful of highly pixelated coins scatter. Inundated with a range of GIFs—in terms of both content and the intensity of that content—the reader is destabilized as they move through the chapter, unable to gain consistency or clarity. Is the fall funny? Is the free fall a release, an assertion of personal freedom or autonomy? Or is the fall simply the prelude to death, existential violence in-motion? As the GIFs repeat in eternal cycles, readers have the option to stay with one scene for as long as they choose, whether that scene evokes shudders or laughter, confusion or captivation, glee or horror. It is profoundly unclear how one is meant to perceive or interpret the GIFs, both as individual parts of the story Cooper is creating, and as composite parts of a broader narrative. The GIFs just propel downwards, forever.
GIFs representing physical violence have an inherent humor to them, one that is specific to the removed position one occupies on the Internet. The painful or life-ending action repeats endlessly with what Cooper considers a “kind of heartlessness” that implies violence regardless of the moment when the GIF cuts off and begins again.[11] The thin veneer of humor obscures but does not entirely erase this strange form of cruelty, regardless of if the user/reader/viewer is cognizant of cruelty as a possibility. This is similar Mellamphy’s articulation of what makes larval warfare larval; rather than appearing as a domineering assertion of power or control, larval warfare makes use of “the appearance of ordinariness,” allowing for an incremental merging with various forms of technical exchange in order to exploit people from within.[11] There is a common reliance on insidiousness and an assumption of ignorance to create desired conditions, regardless of the larger project.
A Future of Fog
For most people, the physicality of violence is what allows them to recognize it as such. It is most easily identified as an immediate sensation, like a person hitting the ground after falling from a great height. Immediacy and observable consequences also determine how “real” the violence is deemed; a woman in a movie being punched in the face is a different kind of violence than a cartoon mouse hitting a cat over the head with an oversized hammer. As Cooper demonstrates that digitally-reproduced violence quickly becomes hazy and requires increased discernment to pin down, Mellamphy articulates how war has undergone a similar obfuscation. Rather than occurring through physical combat between mutually-identified opponents, it can now take place in nonphysical spaces, and be conducted by anonymous actors.
Within the description of larval warfare that Mellamphy provides, it can be argued that Cooper is waging his own “war” on the reader by destabilizing the logics usually relied upon to process and interpret information. When it becomes unclear where the violence begins or ends, or what the consequences of that violence are, is it even violence anymore? Or does it become something else?
Whether in Mellamphy’s context of global armed conflict or Cooper’s fictional violence, one thing remains clear: larval warfare advances by enshrouding itself in a “fog of peace,” through which it wages warfare without “friction or detection.”[12] If we can no longer identify violence or develop new methods for identifying it in its ever-expanding presentations, we risk getting lost in this fog forever—on and offline.
Endnotes
- Mellamphy, Nandita Biswas. Larval Warfare. Video, n.d.
- Mellamphy.
- Mellamphy.
- Mellamphy.
- Mellamphy.
- Mellamphy.
- Mellamphy.
-
Henry, Casey Michael. “How Dennis Cooper Turns GIFs Into Fiction.” The New Yorker, April 9, 2015. https://www.newyorker.com/books/page-turner/how-dennis-cooper-creates-fiction-from-gifs.
- Mellamphy.
- Henry.
- Henry.
- Mellamphy.